Project scaffold
In this section, we will set up the basic structure for our Tic Tac Toe game in Unity. We’ll mock the game mechanics and focus on the layout and design.
Overview
The game will consist of the following elements:
- Game board - A 3x3 grid where players place their marks.
- UI elements - Buttons for each cell in the grid and a text display for game status.
- Game logic - Scripts to manage player turns, check for winners, and handle game state.
Set up the basic layout
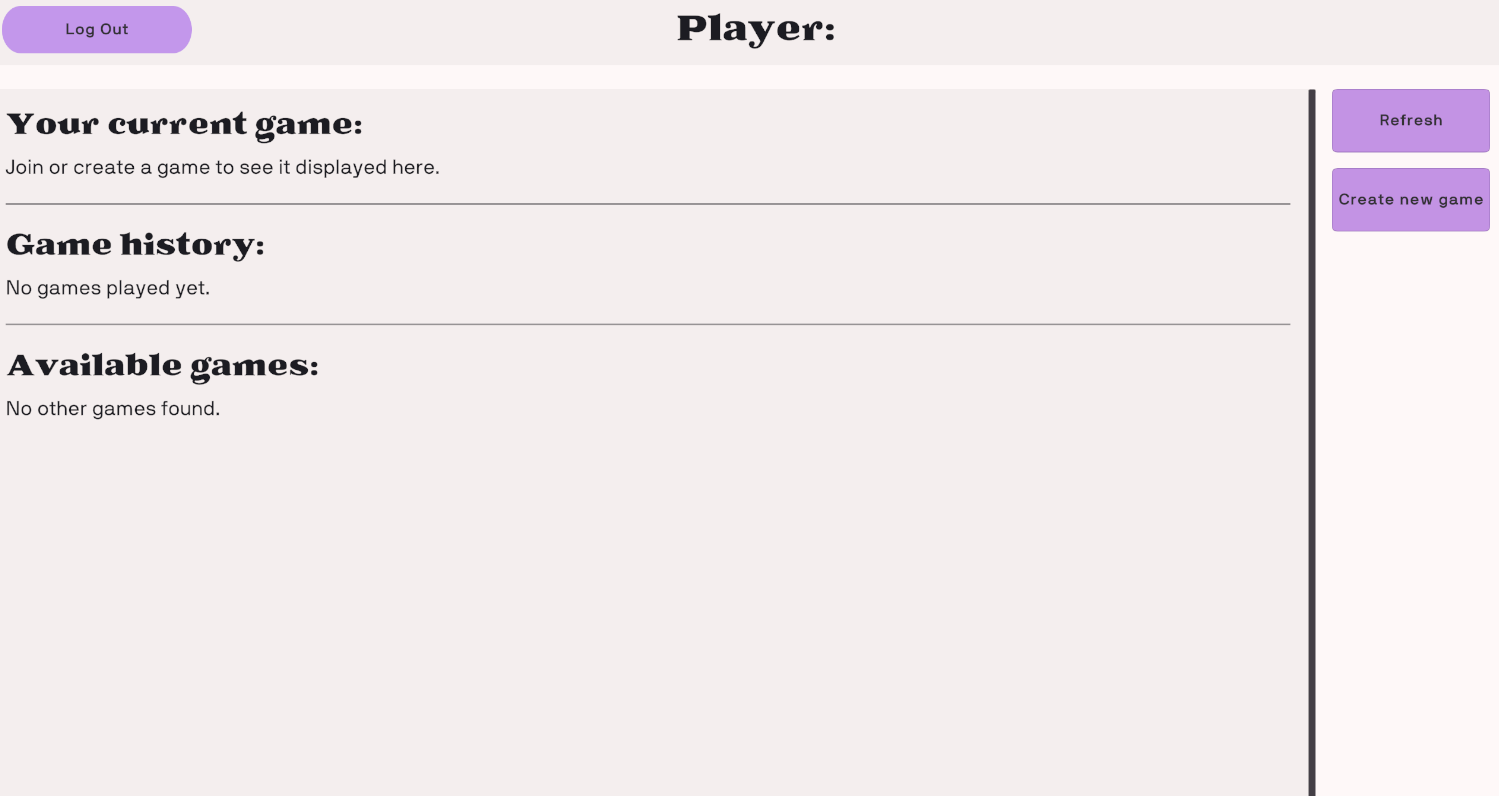
Pages
- Login page
-
Provides options for users to create new accounts or log in with existing credentials.

-
- Lobby page
-
Displays ongoing and completed matches.
-
Allows users to create or join a new match.
-
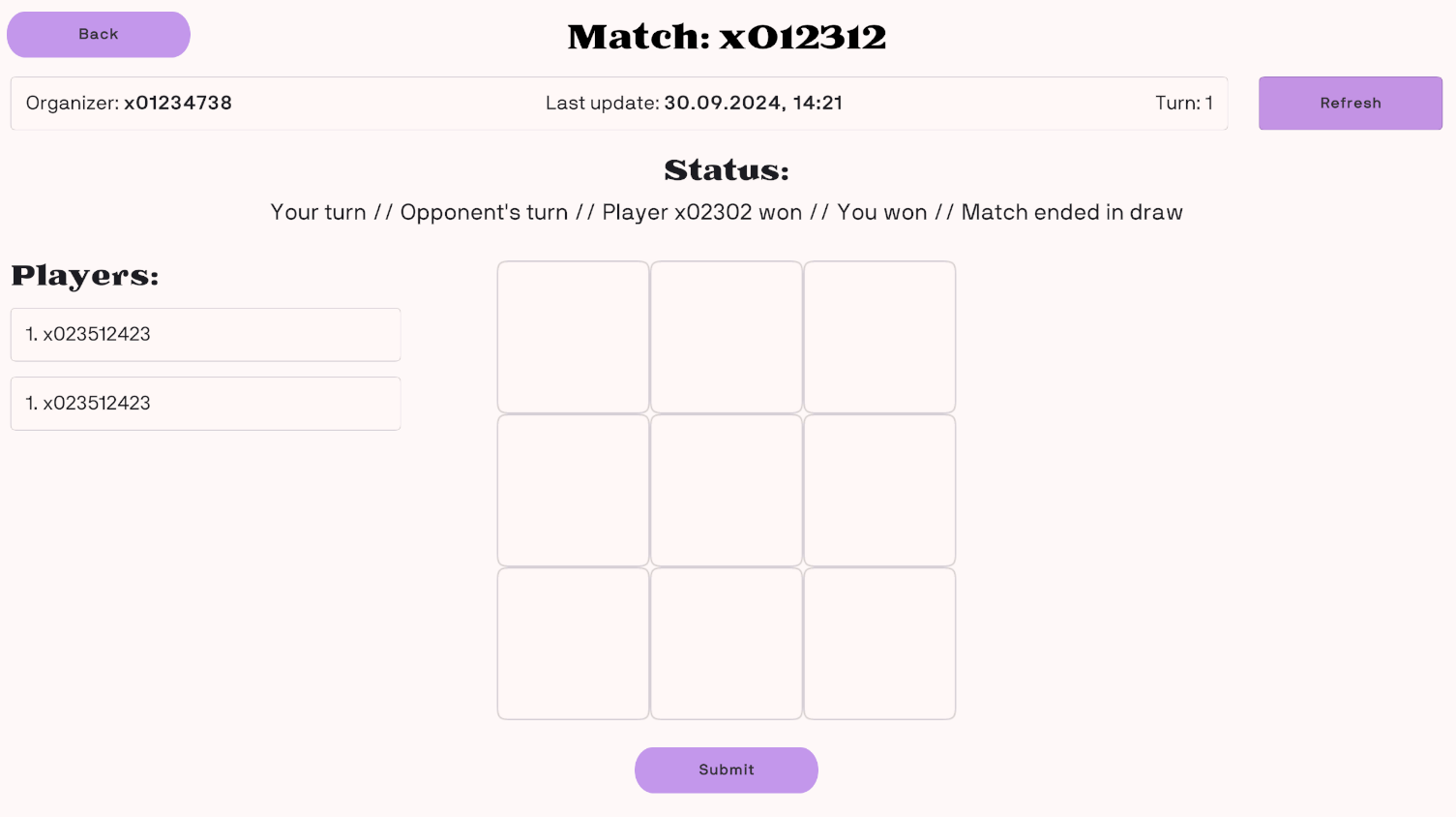
- Game page
-
The main page where the Tic-Tac-Toe game is played.
-
Includes the game board, UI elements, and real-time game updates.
-
Set up the ServiceLocator
The ServiceLocator acts as a centralized hub for initializing and managing all key services and managers in the game. Its goal is to make these services easily accessible to other classes, avoiding repetitive instantiation and improving modularity.
Steps to set up the ServiceLocator:
-
Create a
GameObject:- Create a new empty
GameObjectin your scene in Unity. - Name it something like
ServiceLocatorfor clarity. - Attach the
ServiceLocatorscript to thisGameObject.
- Create a new empty
-
Set script execution order:
-
Go to Edit → Project Settings → Script Execution Order.
-
Add the
ServiceLocatorscript and move it to the top of the list. -
This ensures that the
ServiceLocatoris initialized first, allowing other components to access its services as soon as needed.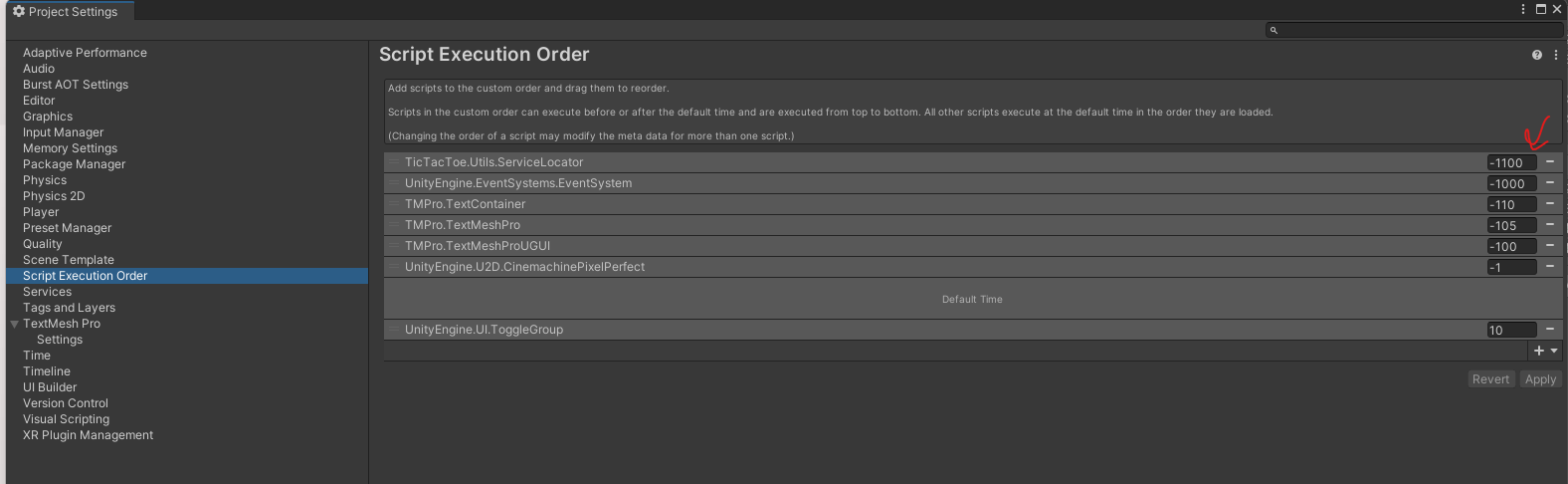
-
-
Understand the role of
ServiceLocator:- Open the
ServiceLocatorscript to examine its components. You'll notice that it initializes instances of various services likeBlockchainService,GameService, andUIManager. These services are documented in the comments of the script. Here's a brief explanation of their functionality:
- Open the
Services in ServiceLocator
-
UIManager:- Manages all UI-related elements in the game, such as menus, notifications, and player interface interactions.
- The
[SerializeField]attribute allows theUIManagerto be assigned through the Unity editor.
[field: SerializeField] public UIManager UIManager { get; private set; } -
LocalStorageService:- Handles saving and retrieving data locally on the player's device.
- For example, it might save player progress, game settings, or cached data.
- It is initialized in the
SetupServices()method:
LocalStorageService = new LocalStorageService();
LocalStorageService.Initialize(); -
BlockchainService:- Manages blockchain-related operations, such as connecting to a blockchain network or performing transactions.
- Blockchain initialization may involve network calls, so it uses asynchronous operations (
await BlockchainService.Initialize()).
BlockchainService = new BlockchainService();
await BlockchainService.Initialize(); -
GameService:- Encapsulates core game logic and interacts with other services (e.g., the blockchain for game state persistence or transactions).
- It depends on the
BlockchainService, which is passed to its constructor during initialization:
GameService = new GameService(BlockchainService);
Create the game board
To begin building the UI for your Tic Tac Toe game, follow these steps:
Set up the UIManager
Start by creating a UIManager to manage different views (pages) in your game. The UIManager will handle transitions between these views and serve as a container for all UI elements.
-
What it does: The
UIManagerwill host multiple views, such as the login screen, game board, and result screens. It will listen for events (e.g., button clicks) to switch between pages. -
Example: For instance, in the
LoginView, you might have a method like this:public async void OnNewAccountButton()
{
var blockchainService = ServiceLocator.Instance.BlockchainService;
var newAccountData = await blockchainService.OpenStrategyRegisterAccount();
}This example creates a new blockchain account using the
BlockchainService.
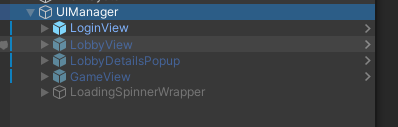
Visualize the structure
-
The UI hierarchy should look something like this:
-
The scripts for managing these views will include logic for handling UI interactions, as shown here:
Set up the game grid in Unity
-
Create an object
- Create an empty
GameViewobject and place it as a child of theUIManagerin theEditorHierarchy.
- Create an empty
-
Add a
Canvas-
In the Hierarchy panel, create a new
Canvas. This will serve as the parent for all your UI elements. -
Ensure the Canvas is set to Screen Space - Overlay for a standard UI setup.
-
-
Add a
GridPanel-
Inside the
Canvas, create aPaneland rename it toGridPanel. -
Adjust its size to match the area you want for the game grid.
-
Add a grid layout
- Select the
GridPanelin the Hierarchy. - Add a Grid Layout Group component from the Inspector.
- Configure the following settings in the Grid Layout Group:
- Cell Size: Set to (100, 100) for uniform cells.
- Spacing: Set to (5, 5) for padding between cells.
- Constraint: Choose Fixed Column Count and set Constraint Count to
3to create a 3x3 grid.
Create buttons for the grid cells
- Under the
GridPanel, create aButtonand rename it to "Cell1". - Adjust the button's size to match the cell dimensions (e.g., 100x100).
- Duplicate this button to create eight more, for a total of nine buttons.
- Rename the buttons sequentially (e.g., "Cell2", "Cell3", and so on).
Add a status text
- In the Canvas, create a
Textelement and position it above theGridPanel. - Rename it to
StatusTextand set its initial text to something like "Player X's Turn". - Adjust the font size, alignment, and color for better visibility.
Connect scripts to the UI
- Write a script (e.g.,
GameView) to control interactions between the UI and game logic. - Add methods for updating the game grid and handling player turns.
- Attach this script to an empty
GameObjectnamedGameView.
Set up Tic Tac Toe game scripts in Unity
Create the scripts folder
- In the Project panel, right-click and select Create > Folder.
- Name the folder
Scriptsto keep your game scripts organized.
Game logic overview
GameViewscript: Manages the game's visual interface, essentially functioning as the UI. It handles button click events and invokes theMakeMove()method in theGameService.GameServicescript: Handles logic related to querying games, submitting turns, and tracking the state of active games.
GameService and GameData
The GameService is responsible for managing active games and their states. It queries games and handles operations like submitting turns. Each fetched game is represented by a GameData model:
/// <summary>
/// The data received from the blockchain queries related to games.
/// </summary>
public class GameData
{
[JsonProperty("id")] public int RowId { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("created_by")] [CanBeNull] public byte[] CreatedBy { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("created_at")] public string CreatedAt { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("player1_account_id")] [CanBeNull] public byte[] Player1 { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("player2_account_id")] [CanBeNull] public byte[] Player2 { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("last_step_account_id")] [CanBeNull] public byte[] LastStepBy { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("last_step_at")] public string LastStepAt { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("winner")] [CanBeNull] public byte[] Winner { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("status")] public GameStatus Status { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("slot_1")] public SlotState Slot1 { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("slot_2")] public SlotState Slot2 { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("slot_3")] public SlotState Slot3 { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("slot_4")] public SlotState Slot4 { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("slot_5")] public SlotState Slot5 { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("slot_6")] public SlotState Slot6 { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("slot_7")] public SlotState Slot7 { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("slot_8")] public SlotState Slot8 { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("slot_9")] public SlotState Slot9 { get; set; }
}
Update slots in GameView
Each cell in the game grid is represented by a TicTacToeSlot component. These slots are updated using the UpdateSlots method in the GameView script:
private void UpdateSlots()
{
var canUserSubmit = _gameData.Status is GameStatus.Active && Buffer.From(_gameData.LastStepBy) != _blockchainService.UserAccountId;
_slots[0].SetData(_gameData.Slot1, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 0));
_slots[1].SetData(_gameData.Slot2, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 1));
_slots[2].SetData(_gameData.Slot3, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 2));
_slots[3].SetData(_gameData.Slot4, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 3));
_slots[4].SetData(_gameData.Slot5, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 4));
_slots[5].SetData(_gameData.Slot6, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 5));
_slots[6].SetData(_gameData.Slot7, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 6));
_slots[7].SetData(_gameData.Slot8, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 7));
_slots[8].SetData(_gameData.Slot9, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 8));
}
Implement the GameView script
The GameView handles interactions between players and updates the game board:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using _TicTacToe.Scripts.Models;
using Chromia;
using TicTacToe.Services;
using TicTacToe.Utils;
using TMPro;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;
namespace TicTacToe.UI
{
/// <summary>
/// The main game view where users play Tic-Tac-Toe and can submit turns.
/// </summary>
public class GameView : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField] private TMP_Text _header;
[SerializeField] private TMP_Text _organizerText;
[SerializeField] private TMP_Text _lastActionAtText;
[SerializeField] private TMP_Text _currentTurnText;
[SerializeField] private TMP_Text _player1;
[SerializeField] private TMP_Text _player2;
[SerializeField] private TMP_Text _gameStatus;
[SerializeField] private List<TicTacToeSlot> _slots;
[SerializeField] private GameObject _submitButton;
[SerializeField] private Button _refreshButton;
private UIManager _uiManager;
private GameService _gameService;
private BlockchainService _blockchainService;
private GameData _gameData;
private int _slotToSubmit = -1;
private void OnEnable()
{
_uiManager ??= ServiceLocator.Instance.UIManager;
_gameService ??= ServiceLocator.Instance.GameService;
_blockchainService ??= ServiceLocator.Instance.BlockchainService;
}
public void SetData(GameData gameData)
{
_gameData = gameData;
UpdateView();
}
public void OnBackButton()
{
_uiManager.OpenLobby();
}
public void OnRefreshButton()
{
Refresh();
}
public async void OnSubmitButton()
{
if (_slotToSubmit < 0)
return;
_uiManager.ToggleLoadingSpinner(true);
var success = await _gameService.MakeMove(_gameData.RowId, _slotToSubmit);
_uiManager.ToggleLoadingSpinner(false);
if (success)
Refresh();
}
private async void Refresh()
{
_uiManager.ToggleLoadingSpinner(true);
_gameData = await _gameService.GetGameById(_gameData.RowId);
_uiManager.ToggleLoadingSpinner(false);
UpdateView();
}
private void UpdateView()
{
_header.text = $"Match: {_gameData.RowId}";
_organizerText.text = $"Organizer: <b>{UIUtils.GetShortenedAccountId(_gameData.CreatedBy)}";
_lastActionAtText.text = $"Last update: <b>{UIUtils.GetUnixTimestamp(_gameData.LastStepAt)}";
_currentTurnText.text = $"Turn: {UIUtils.GetTurn(_gameData)}";
var isUserPlayer1 = Buffer.From(_gameData.Player1) == _blockchainService.UserAccountId;
_player1.text = $"1. {UIUtils.GetShortenedAccountId(_gameData.Player1)} ( <b>{(isUserPlayer1 ? "You" : "Opponent")} ) <color=purple> O";
_player2.text = $"2. {UIUtils.GetShortenedAccountId(_gameData.Player2)} ( <b>{(isUserPlayer1 ? "Opponent" : "You")} ) <color=purple> X";
_gameStatus.text = UIUtils.GetGameStatus(_gameData, _blockchainService.UserAccountId);
_submitButton.SetActive(false);
_slotToSubmit = -1;
_refreshButton.interactable = _gameData.Status is GameStatus.Active;
UpdateSlots();
}
private void UpdateSlots()
{
var canUserSubmit = _gameData.Status is GameStatus.Active && Buffer.From(_gameData.LastStepBy) != _blockchainService.UserAccountId;
_slots[0].SetData(_gameData.Slot1, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 0));
_slots[1].SetData(_gameData.Slot2, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 1));
_slots[2].SetData(_gameData.Slot3, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 2));
_slots[3].SetData(_gameData.Slot4, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 3));
_slots[4].SetData(_gameData.Slot5, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 4));
_slots[5].SetData(_gameData.Slot6, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 5));
_slots[6].SetData(_gameData.Slot7, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 6));
_slots[7].SetData(_gameData.Slot8, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 7));
_slots[8].SetData(_gameData.Slot9, canUserSubmit, (isSelected) => OnSelected(isSelected, 8));
}
private void OnSelected(bool isSelected, int index)
{
_submitButton.SetActive(isSelected);
if (isSelected)
{
_slotToSubmit = index + 1; // Blockchain expects values from 1 to 9
// Unselect all other slots
for (int i = 0; i < _slots.Count; i++)
{
if (i == index) continue;
_slots[i].SetSelected(false);
}
}
}
}
}
Set up the game logic
- Attach the
GameViewscript:- Create an empty
GameObjectin the Hierarchy, name itGameView. - Drag and drop the
GameViewscript onto thisGameObject. - Assign the
cellsarray (game grid buttons) andstatusTextfield in the Inspector.
- Create an empty
- Complete the win logic:
- Implement logic in the
CheckForWinnermethod to detect winning combinations and update the game state.
- Implement logic in the
Test and refine
- Run the game:
- Click the Play button in Unity to test the setup.
- Verify grid updates, player turns, and game status changes.
- Debug:
- Resolve any issues with game mechanics.
- Enhance:
- Add features like animations, sound effects, or a restart button for better gameplay.